As an advertiser, your goal is clear: to ensure your marketing efforts resonate with your target audience. After all, success lies in engaging individuals who genuinely are interested in the products and services you have to offer.
Yet, with the impending farewell of cookies, traditional tracking methods are undergoing a transformation. In this evolving landscape, contextual targeting re-emerges as a cornerstone strategy. By focusing on the context in which content is consumed, you can deliver ads that not only capture attention but also foster genuine engagement.
In this guide, we'll delve into the intricacies of mastering contextual targeting, providing actionable insights to craft campaigns that precisely align with the interests and intent of your audience. Join us on this journey towards more effective, relevant and impactful advertising.

What is Contextual Targeting?
Contextual targeting is a digital advertising strategy that involves placing ads in front of users based on the content they are currently consuming.
Unlike traditional methods that rely on user data and cookies, contextual targeting assesses the context and subject matter of a webpage to determine the most relevant ads to display. This approach ensures that advertisements are aligned with the viewer’s interests at that specific moment.
For example, if a user is reading an article about travel destinations, contextual targeting would display ads related to travel, tourism or related products and services. This method is becoming increasingly desirable as the industry shifts away from cookie-based tracking due to privacy concerns.
Contextual targeting comes in various forms, each tailored to different aspects of content and user behavior. Here are the main types.
- Keyword contextual targeting: This method involves targeting ads based on specific keywords present within the content or search queries. It's one of the most straightforward forms of contextual targeting.
- Category contextual targeting: Advertisers choose predefined categories or topics that align with their products or services. Ads are then displayed on pages that fall within those chosen categories.
- Semantic contextual targeting: This method uses Natural Language Processing (NLP) algorithms to understand the context and meaning of words and phrases on a webpage. It's more sophisticated than simple keyword targeting.
How Does Contextual Targeting Work?
Contextual targeting works by analyzing the content of a webpage to understand its subject matter and context. Below is a step-by-step process on how this solution operates.
- Page crawling and content analysis: First, a contextual targeting system crawls a web page to analyze the text, images and other elements on the page.
- Keyword extraction: It identifies and extracts keywords and key phrases from the content. These keywords are crucial in understanding the page’s main topics and themes.
- Category assignment: The system then assigns categories or topics to the page based on the extracted keywords. For instance, if the keywords include "travel," "beaches," and "vacation," the assigned category might be "Travel & Tourism."
- Ad matching: The system matches relevant ads with the identified category — advertisers would have set their ads with specific categories or keywords prior to this action.
- Ad placement: Finally, when a user visits that webpage, the system selects an ad from the category pool and displays it on the page.
The key advantage of contextual targeting is that it doesn't rely on individual user data. Instead, it focuses on the content the user is currently consuming, ensuring that the ads are directly related to what they are interested in at that moment.
In addition, this method respects user privacy and aligns with evolving privacy regulations, making it a critical strategy in the post-cookie era.

How to Implement Contextual Targeting?
Are you ready to implement context targeting in your next campaign? Fortunately, the steps for setting up contextual targeting are quite simple.
- Define campaign objectives: Clearly outline the goals and objectives of your advertising campaign. This will guide your contextual targeting strategy.
- Select a contextual targeting method: Choose the contextual targeting method that best aligns with your campaign objectives (e.g., keyword, category, semantic).
- Get your ad matched to relevant content: Google or another ad network identifies high-performing placements on websites that align with your contextual targeting criteria.
- Monitor, analyze and optimize: Monitor the performance of your campaign, analyze key metrics and optimize it. This may include refining keywords, adjusting bidding strategies or modifying ad creatives.
By following these steps, you can effectively implement contextual targeting to reach your target audience with relevant and engaging content.

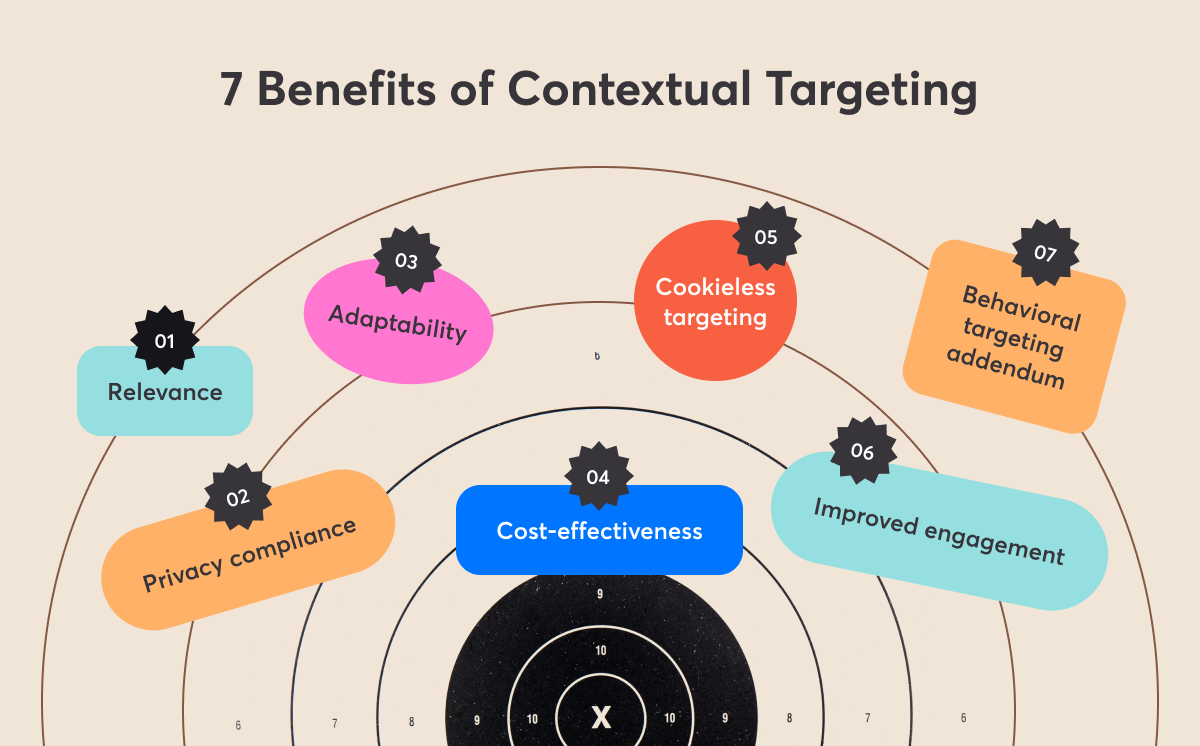
The Benefits of Contextual Targeting
Contextual targeting offers a range of benefits for advertisers looking to reach their target audience effectively.
- Relevance: Contextual targeting allows advertisers to display their ads alongside content that is directly relevant to their products or services. This increases the likelihood of capturing the attention of interested users.
- Privacy compliance: Unlike some other targeting methods that rely on user data, contextual targeting does not involve collecting or using personal information. This aligns with privacy regulations and helps maintain user trust.
- Adaptability: Contextual targeting is versatile and can be applied across various content types and platforms, whether on websites, blogs, videos or social media.
- Cookieless targeting: As cookies face increasing scrutiny and restrictions, contextual targeting provides an alternative method to deliver relevant ads without relying on third-party cookies.
- Cost-effectiveness: Contextual targeting can often be a cost-effective solution, as it doesn't involve the data acquisition and management costs associated with other targeting methods.
- Improved engagement: When ads are displayed in relevant contexts, users are more likely to engage with them, leading to higher click-through rates and better overall campaign performance.
- Complementary: Contextual targeting can work in conjunction with other targeting methods (e.g., behavioral targeting), providing an additional layer of precision to reach the right audience.
In addition to these advantages, we can add several more benefits thanks to our proprietary contextual targeting solution: Contextual Intelligence.
- Natural privacy protection: MGID utilizes first-party contextual data from our trusted publisher partnerships, steering clear of personal data. Our Contextual Intelligence solution combines content elements, sentiment analysis and audience interests without relying on personal information.
- Empowering publishers: By prioritizing context in targeting decisions, advertisers empower publishers. This allows publishers to align their editorial strategies with advertiser demands. Contextual Intelligence opens opportunities for niche publishers to connect with specific audiences and boost ad revenue.
- Premium advertiser reach and revenue maximization: MGID helps to ensure global and local advertisers reach their desired audiences. Simultaneously, we enable publishers to monetize their content by offering inventory to top-bidding advertisers. Contextual targeting, especially for brand awareness campaigns, leads to higher eCPMs, benefiting both advertisers and publishers.
By harnessing the power of contextual targeting, advertisers can effectively connect with their desired audience in a way that is privacy-friendly, relevant and aligned with the content they consume. This leads to more engaging and successful advertising campaigns.
Actionable Tips for Effective Contextual Targeting Campaigns
By applying these tips, you'll be able to run contextual targeting campaigns that effectively reach and engage your target audience.
- Research keywords: Start by conducting extensive keyword research to identify the most relevant and high-performing keywords for your campaign. Tools like Google's Keyword Planner are immensely helpful.
- Define your negative keywords: Another equally important tip is to identify your negative keywords. These are words or phrases that you don't want associated with your ads. This helps in avoiding irrelevant placements.
- Leverage contextual categories: Many advertising platforms offer contextual categories or topics. Utilize these options to narrow down your targeting to specific content categories that align with your campaign.
- Tailor ad copy to context: Create ad content that seamlessly blends in with the context of the page. Ensure that the messaging and imagery are relevant to the content surrounding it.
- Utilize dynamic keyword insertion: Some platforms allow dynamic keyword insertion, which automatically inserts the keyword that triggered the ad. This makes your ad more relevant to the user's search.
- Set specific landing pages: Direct users to landing pages that are highly relevant to both the ad content and the page they left. This improves user experience and conversions.
- Regularly review placements: Keep a close eye on where your ads are appearing. Exclude placements that aren't performing well or are not aligned with your campaign goals.
- Utilize remarketing with contextual targeting: Combine contextual targeting with remarketing to re-engage users who have previously visited your website. Show them contextually relevant ads based on their previous interactions.
- Monitor performance metrics: Track key performance indicators (KPIs) like click-through rates (CTR), conversion rates and return on ad spend (ROAS). Use these insights to optimize your campaign.
- A/B test ad variations: Experiment with different ad variations to see which one resonates best with your audience. Test headlines, ad copy and imagery.
- Adapt to seasonal trends: Tailor your contextual targeting strategy to align with seasonal trends and events. This helps increase relevance and engagement during specific times of the year.
- Stay updated on industry trends: Keep abreast of new developments and technologies in contextual targeting. This allows you to incorporate the latest strategies for improved campaign performance.

Contextual Targeting Challenges and Pitfalls
Let's dive into the challenges and potential pitfalls associated with contextual targeting, as well as how to address them.
1. Keyword ambiguity
Some keywords may have multiple meanings, leading to ads being displayed on irrelevant content.
Solution: Utilize negative keywords to exclude placements where your ad's context might be misinterpreted.
2. Limited control over placements
In some cases, advertisers may have limited control over the specific websites or pages where their ads appear.
Solution: Regularly review placement reports and exclude websites or categories that aren't performing well or aligned with your campaign goals.
3. Brand safety concerns
There's a risk of ads appearing alongside content that is controversial, offensive or not in line with a brand's values.
Solution: Implement strict brand safety measures, use exclusion lists and work with platforms that offer robust brand safety tools.
4. Ad placement cannibalization
Multiple ads from the same advertiser might compete for placement on a single page, potentially driving up costs without delivering proportionate results.
Solution: Utilize ad frequency capping to control how often your ads are shown to the same user on a single page.

Contextual Targeting vs. Audience Targeting: What's the Difference?
Are contextual targeting and audience targeting effectively the same solution? The short answer is no. The more detailed answer is below.
Contextual targeting:
- Focuses on placing ads in environments that are contextually relevant to the content of a webpage;
- Analyzes the keywords, topics and themes of the page to determine ad placement;
- Does not rely on specific user data or behavior and instead targets based on the content context;
- Is well-suited for brand awareness campaigns and reaching users in the right context.
Audience targeting:
- Involves targeting specific groups of users based on their demographics, interests, behaviors or other characteristics;
- Utilizes data collected about users' browsing habits, preferences and interactions online;
- Allows for more precise targeting of individuals or segments with a higher likelihood of conversion;
- Is effective for campaigns that aim to reach a particular demographic or retarget users based on previous interactions.
In essence, while contextual targeting focuses on the content environment, audience targeting hones in on individual user attributes and behaviors.
However, it is important to understand that audience targeting heavily relies on collecting and utilizing cookies. On the contrary, contextual targeting, in particular, Contextual Intelligence solution from MGID, uses machine learning to navigate the cookieless landscape. We train our system by curating and testing hundreds of URLs for accuracy. This feature automatically recognizes topics on any page. Plus, it ranks pages by relevance, ensuring bids are proportional. This approach leads to full-scale contextual campaigns with higher ROAS.

Contextual Targeting in Action: Examples of Famous Brands
Here are a few examples of popular brands that have successfully implemented contextual targeting in their advertising campaigns.
Nike
- Context: During major sporting events like the Olympics or World Cup
- Strategy: Nike runs ads featuring athletes and sports-related content on sports news websites, social media platforms and streaming services during these events. This ensures they reach an audience highly interested in sports.
Amazon
- Context: Product recommendations based on browsing and purchase history
- Strategy: Amazon uses browsing and purchase history data to recommend related products to users. For example, if you buy a camera, they might suggest camera accessories or photography books.
Spotify
- Context: Personalized playlists and music recommendations
- Strategy: Spotify uses data on users' listening habits to curate personalized playlists and suggest new music from similar genres or artists. This keeps users engaged and encourages longer platform usage.
- Context: Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs) and Display Network
- Strategy: Google's contextual targeting analyzes the content of a webpage to determine the most relevant ads to display. For example, if a user searches for hiking boots, they might see ads for outdoor gear stores.
Airbnb
- Context: Location-based recommendations
- Strategy: When users search for accommodations in a specific city or neighborhood, Airbnb uses contextual targeting to display listings in that area, ensuring relevance to the user's search.
FAQ
What is contextual targeting?
Contextual targeting is an advertising strategy that involves placing ads in environments that are contextually relevant to the content. It targets users based on the content they're currently viewing rather than their personal data.
How does contextual targeting work?
Contextual targeting analyzes the content of a webpage or digital environment in real time. It identifies keywords, themes and other contextual cues to match relevant ads with the content, creating a seamless and relevant user experience.
Is contextual targeting compliant with privacy regulations?
Yes, contextual targeting doesn't rely on collecting or using personal data. It aligns with privacy regulations, making it a privacy-friendly alternative to other targeting methods that involve user data.
How can advertisers implement contextual targeting effectively?
To implement contextual targeting, advertisers need to set campaign parameters, ensure that their advertising content aligns with relevant content and select appropriate placements for their ads.
What are the benefits of using contextual targeting?
Contextual targeting offers a wide range of advantages, such as increased relevance, privacy compliance, adaptability across platforms, brand safety and cost-effectiveness. It also complements other targeting methods for improved precision.
Can contextual targeting be used on platforms other than Google?
Yes, contextual targeting can be implemented across various advertising networks and platforms and is not limited to Google. Many advertising platforms such as MGID offer contextual targeting options and their own solutions like MGID’s Contextual Intelligence.
How does contextual targeting adapt to changes in user behavior and content trends?
Contextual targeting relies on real-time analysis of content, allowing it to adapt dynamically to shifts in user behavior and content trends. This ensures that ads remain relevant and effective even as online environments evolve.
Conclusion
Contextual targeting is the cornerstone of effective advertising in today's evolving digital landscape. It ensures your message aligns with the content users are actively engaged with, offering both relevance and respect for their browsing experience.
At MGID, we've harnessed this power through our native advertising platform, reaching over 900 million monthly users. Our Contextual Intelligence solution goes beyond industry standards, using AI algorithms to precisely evaluate content context and sentiment.
Join us at MGID, where contextual targeting is not just a service but a strategic advantage that propels your campaigns towards unprecedented success. Register now and unlock the full potential of Contextual Intelligence.





